
Here's why astronauts age slower than the rest of us here on Earth
Time feels like one of the only constants in life — it passes day after day at the same pace.
Then Albert Einstein had to go and ruin that for us.
We've all heard the phrase that "time is relative," but it can be difficult to wrap the mind around what that actually means.
The phrase came from Einstein's Theory of Relativity that joined space and time and created the idea of a fabric that permeates the whole universe: "space-time."
We all measure our experience in space-time differently. That's because space-time isn't flat — it's curved, and it can be warped by matter and energy.
So depending on our position and speed, time can appear to move faster or slower to us relative to others in a different part of space-time. And for astronauts on the International Space Station, that means they get to age just a tiny bit slower than people on Earth.
That's because of time-dilation effects. First, time appears to move slower near massive objects because the object's gravitational force bends space-time.
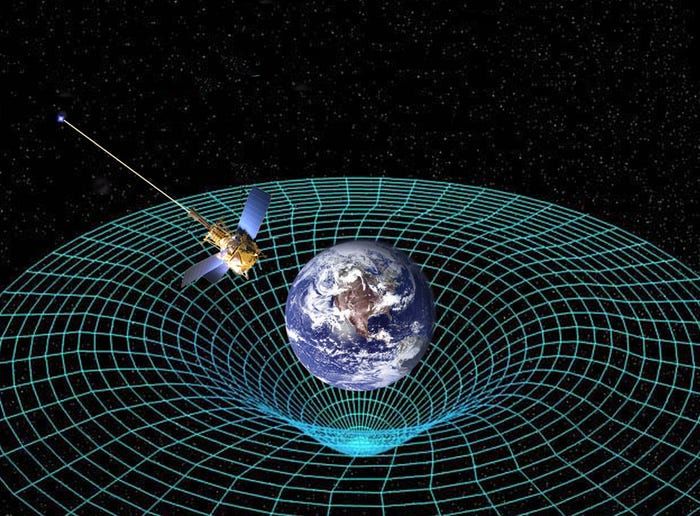
That's why time passes slower for objects closer to the center of the Earth where the gravity is stronger.
That doesn't mean you could spend your life in a basement, just to outlive the rest of us here on the surface. The effect isn't noticeable on such a small scale. If you became a basement hermit, then across your entire lifetime you'd only age a fraction of a second slower than everyone else above ground.
But this concept gets pretty crazy when you start thinking about it:
* A watch strapped to your ankle will eventually fall behind one strapped to your wrist.
* Your head technically ages more quickly than your feet.
* Time passes faster for people living on a mountain than those living at sea level.
Time gets even weirder though.
The second factor is something called "relative velocity time dilation" where time moves slower as you move faster.
The classic example of this is the twin scenario. One twin blasts off in a spaceship traveling close to the speed of light, and one twin stays behind on Earth. When the space-traveling twin returns to Earth, she's only aged a couple years, but she's shocked to find that her Earth-bound sister has aged over a decade.
Of course no one has performed that experiment in real life, but there's evidence that it's real. When scientists launched an atomic clock into orbit and back — while keeping an identical clock here on Earth — it returned running ever so slightly behind the Earth-bound clock.
Then time gets even more complicated because gravitational time dilation and relative velocity time dilation can happen at the same time. A good way to think about it is to consider the astronauts living on the International Space Station.
Currently, an international crew of seven live and work aboard the ISS, orbiting Earth about every 90 minutes, according to NASA.
They're floating about 260 miles above, where Earth's gravitational pull is weaker than it is at the surface. That means time should speed up for them relative to people on the ground. But the space station is also whizzing around Earth at about nearly five miles per second.
That means time should also slow down for the astronauts relative to people on the surface.
You'd think that might even out, but actually their velocity time dilation has a bigger effect than their gravitational time dilation, so astronauts end up aging slower than people on Earth.
The difference isn't noticeable though — after spending six months on the ISS, astronauts have aged about 0.005 seconds less than the rest of us.
That means that when former NASA astronaut Scott Kelly returned home in 2016 from his history-making, year-long stay on the ISS, he technically was 0.01 second younger than his twin astronaut brother — and now US senator — Mark Kelly who stayed on Earth.
So the next time you find yourself wishing the weekend would last longer, stay low to the ground and move really fast. It won't feel like your weekend got any longer, but technically you may gain a teeny, tiny fraction of a fraction of a second.
Remember, time is relative.










