
Huge plan to map the DNA of all life in British Isles
Seventy thousand species.
That’s the best guess for the tally of life, including plants, animals and fungi, found in Britain and Ireland.
And it’s the target of one of biology's most ambitious projects - scientists want to map the DNA of every single one of these organisms.
Having these genomes - each a complete set of genetic information for a species - could transform how we understand the natural world. And there could be benefits for us too in the hunt for nature-inspired medicines and materials.
In Plymouth, the starting point for this immense task is some thick, sticky mud.
Sediment scooped up from the bottom of the Plymouth Sound has been hoisted onto the deck of the research vessel that belongs to the Marine Biological Association.
It's placed in a sieve and hosed off, revealing a host of wriggling creatures.
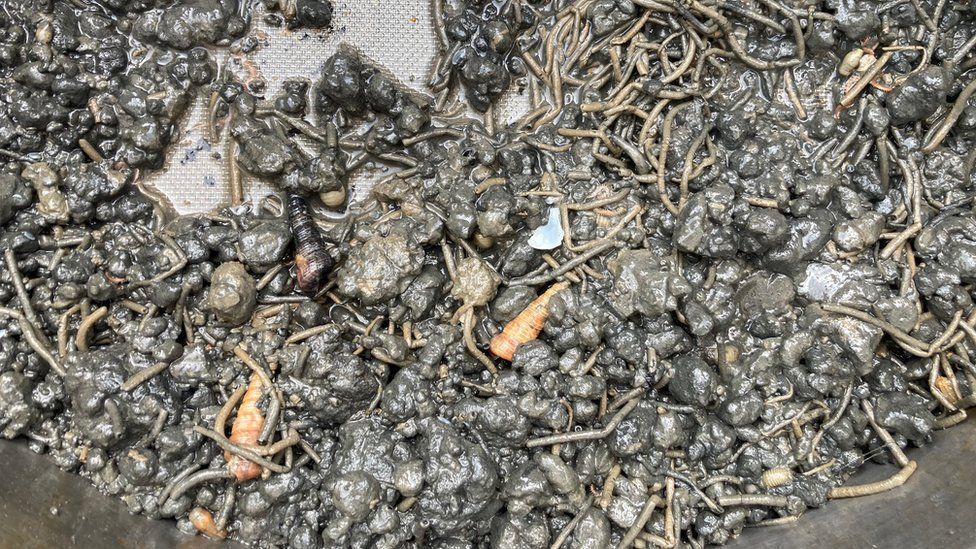 The sediment in Plymouth is jam packed with life
The sediment in Plymouth is jam packed with life
"You can see we've got some bivalves, which are related to clams and mussels. We've also got a gastropod shell - these are quite similar to terrestrial garden snails. And we've got some brittle stars. So lots of different taxa (groups of organisms), lots of different types of animals, which is great," explains marine biologist Patrick Adkins.
Today he's focussing on marine worms known as polychaetes, and there are lots living in the sediment.
Some look like earthworms and others are covered in tiny bristles, squiggling about. But the weirdest is the mud owl. If you squint, its markings look a bit like the face of an owl, until it extends a tubular proboscis, shattering the illusion.
All of them will have their genomes sequenced for the project, which is called the Darwin Tree of Life and includes participation from the Natural History Museum.
"Even if you look at polychaetes, which is just one group of worms, it's a big task with hundreds and hundreds of species," Patrick says.
"We've now got over 100 species of polychaetes collected - it seems like a lot, but really, it's just the beginning."
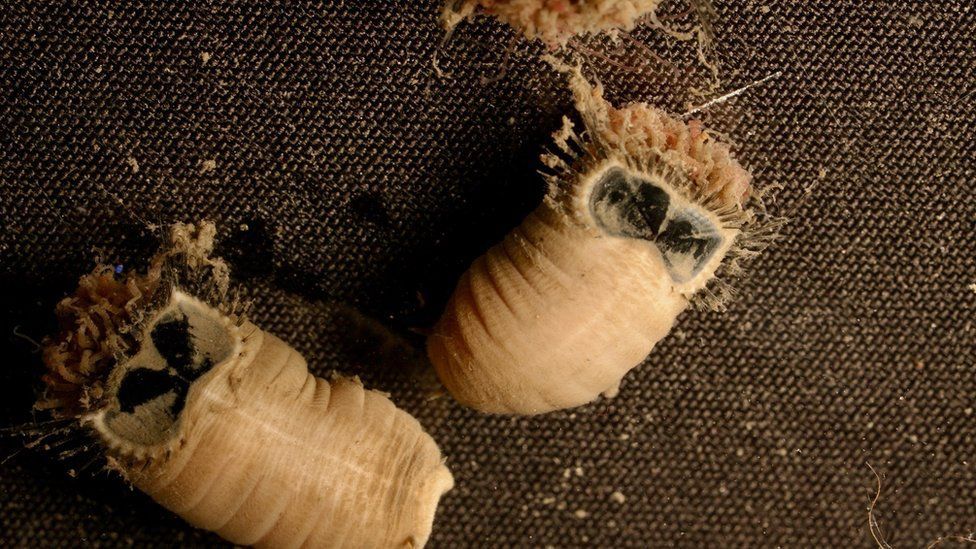 These marine worms are known as mud owls
These marine worms are known as mud owls
The research covers every kind of habitat.
In Oxfordshire, woodlands are the focus.
As dusk falls, a family of badgers emerge from their sett. They snuffle around in the gloom, hunting for some snacks after their sleep.
The animals here in Wytham Woods have been studied in detail for more than 30 years, but now their genome has just been sequenced too.
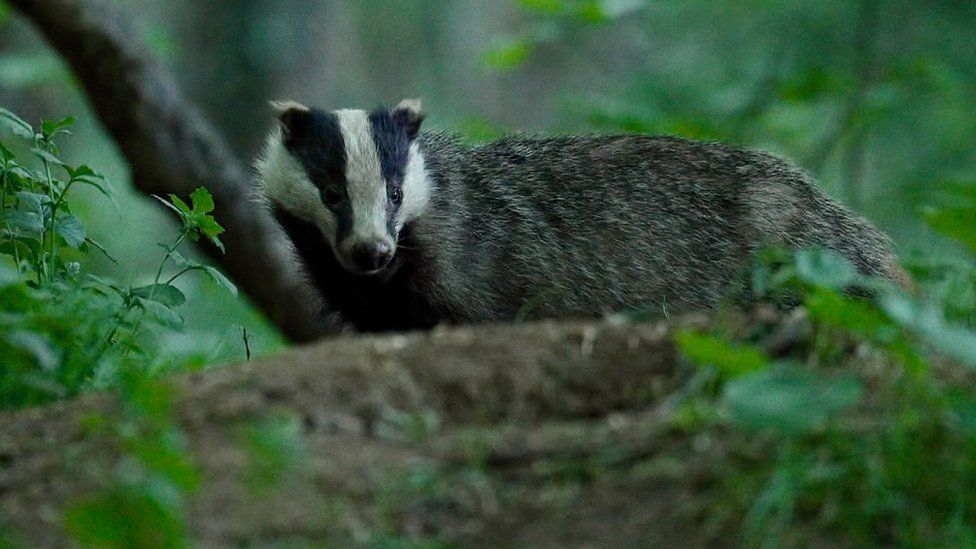 The genome of the European badger has now been sequenced as part of the project
The genome of the European badger has now been sequenced as part of the project
"The genome can answer so many questions that we couldn't answer before," says Ming-Shan Tsai from the University of Oxford.
"We can explore why the badger is very different from other animals - and their unique behaviour."
This includes the puzzle of delayed implantation, where badgers mate and an egg is fertilised, but the process of pregnancy is put on hold until it's the best time of year to have a cub.
"Getting a genome will also help us to understand why badgers are more susceptible to tuberculosis, for example, than other animals," she added.
At the centre of this project is the Wellcome Sanger Institute in Cambridge.
Every day, samples from all over the British Isles are arriving.
Whether it's a leaf from a tree, or some blood taken from an animal, the material is weighed, then frozen with liquid nitrogen, and finally pulverised into a fine powder. From this, the DNA can be extracted, and the genome sequenced.
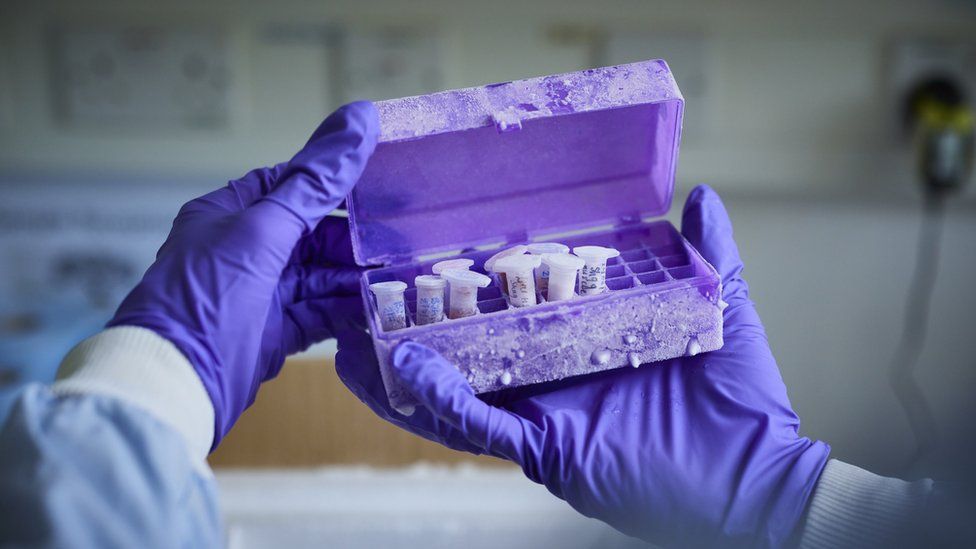 The samples are sent to the Wellcome Sanger Institute
The samples are sent to the Wellcome Sanger Institute
Sanger played a leading role in the human genome project, which took years to complete. Now sequencing a species takes a few days.
Mark Blaxter, who leads the Tree of Life project, says: "When the human genome was sequenced, it changed the way we do human biology forever. And it's really transformed how we see ourselves and how we work with our health and illness.
"And we want to make that possible for all of biology. So we want everybody, working on any species, or any group of species, anywhere in the world, able to have this ultimate foundation."
The genetic work should show how species relate to each other, and reveal their similarities and also where their differences lie.
"It's filling up the library of life," Mark explains.
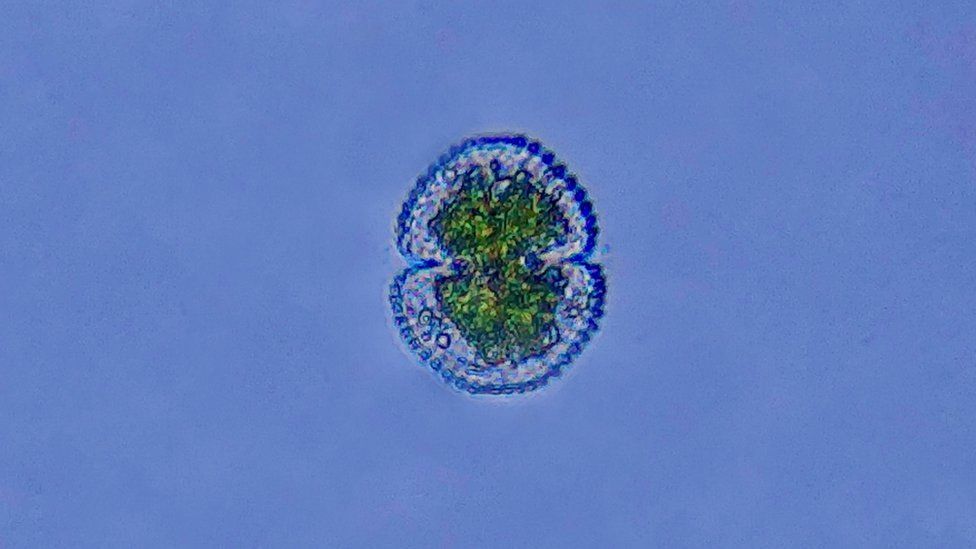 This single-celled organism was found in some pond water
This single-celled organism was found in some pond water
But the tiniest life forms are posing the biggest challenges.
Jamie McGowan, from the Earlham Institute in Norwich, is staring through a microscope at a single drop of pond water. It’s full of single-celled organisms known as protists.
"There's two little green cells here - they're both micro algae. They're photosynthetic, just like plants," he says.
They are the smallest organisms being sequenced for the project, but it's not easy.
"They're really hard to identify, because some of them look really similar. And they're hard to sequence too because they're starting off with really, really tiny amounts of DNA."
Life on Earth began with single-celled organisms, and we could not exist without them.
"We completely depend on them to survive," Jamie explains.
"Protists occupy a really important position in the food chain, where they eat organisms that are smaller than them, such as bacteria and viruses. And then they, in turn, get eaten by larger organisms.
"And quite a lot of protists can produce oxygen - in fact they actually produce about half of the planet's oxygen supply.
"So having their genome sequenced is really important to be able to identify them. Their biodiversity is so poorly understood. And we need to protect them, because they're so critical for all of the rest of life."
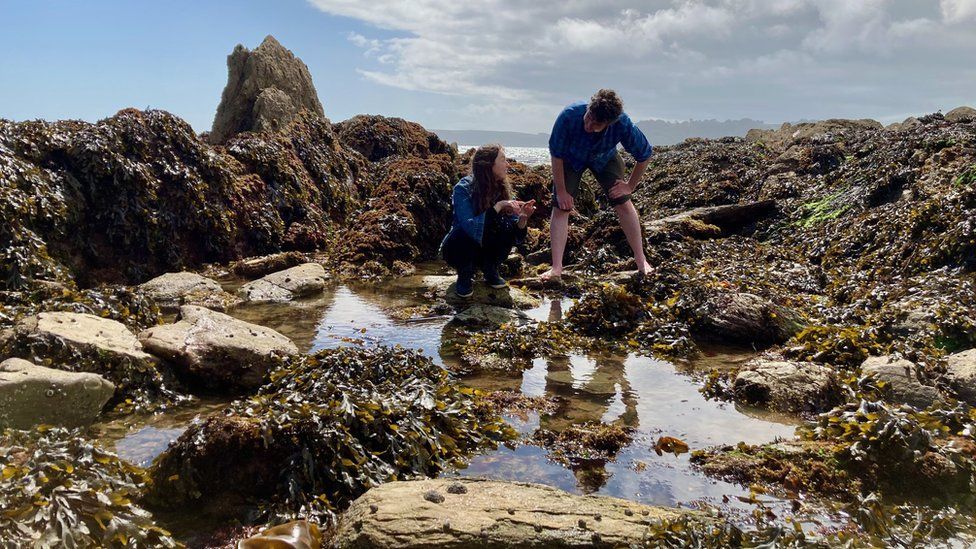 Rock pools hold many different species which could help to inspire nature-based medicines or materials
Rock pools hold many different species which could help to inspire nature-based medicines or materials
Back in Plymouth, and the marine biologists have moved onshore to take a look inside some rock pools.
Each is a colourful microcosmos, containing a multitude of species.
Something flashes past the seaweed.
"It’s a pipefish," says Kes Scott-Somme, a research assistant on the Darwin Tree of Life project. "It's basically like a stretched-out seahorse. They're beautiful - and they're very, very well adapted to their environment. They can live quite high on the shore like this."
But learning about the DNA of creatures like this won't just help us to better understand the species - it could also help us.
"Marine environments are incredibly volatile, and so the animals that live here have to be even more adapted to their space than we are. And that means that they have very specific ways of coping with their environment," says Kes.
"This could help us to find things like antibiotics, medicines and materials. The marine environment is a great place to look for that information."
The Darwin Tree of Life project has a tough deadline - all 70,000 species sequenced by the end of 2030.
There is a lot of work to do, but this project could give us our most detailed understanding yet of the diversity of life.










